Pompe disease (PD) or type II glycogen storage disease (GSDII) or acid maltase deficiency (AMD) is a rare, chronic, weakening and often fatal neuromuscular pathology with a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes depending on onset age. PD is classified into two forms: infantile (Infantile Onset Pompe Disease, IOPD) and late (Late Onset Pompe Disease, LOPD), that can occur in youth or adulthood. IOPD, with onset at birth or within the first few months of life, is characterized by cardiomyopathy and muscle hypotonia (floppy baby or rag dolls) and is more severe than LOPD.
IOPD can cause death in the first year of life, without early diagnosis and treatment. LOPD differs widely depending on onset age and patient’s specific conditions, resulting in a progressive muscle weakness that leads to motor difficulties and respiratory failure over time.
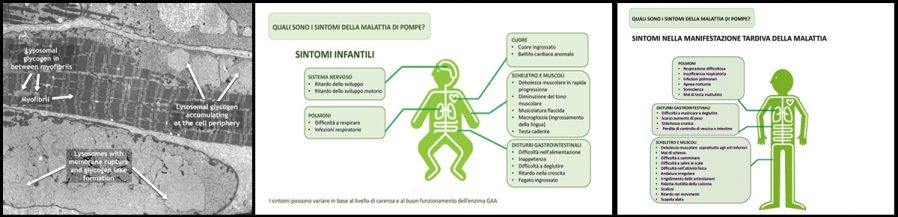
Pompe disease (PD) or type II glycogen storage disease (GSDII) or acid maltase deficiency (AMD) is a rare, chronic, weakening and often fatal neuromuscular pathology with a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes depending on onset age. PD is classified into two forms: infantile (Infantile Onset Pompe Disease, IOPD) and late (Late Onset Pompe Disease, LOPD), that can occur in youth or adulthood. IOPD, with onset at birth or within the first few months of life, is characterized by cardiomyopathy and muscle hypotonia (floppy baby or rag dolls) and is more severe than LOPD.
IOPD can cause death in the first year of life, without early diagnosis and treatment. LOPD differs widely depending on onset age and patient’s specific conditions, resulting in a progressive muscle weakness that leads to motor difficulties and respiratory failure over time.
In newborns, early and timely diagnosis is very important as without treatment, death occurs within the first year of life. An analysis of Pompe registry data shows a diagnosis delay for all PD patients; different diagnostic tests can be performed for the crucial PD early diagnosis.
The main tool for diagnosis is GAA enzymatic activity analysis on DBS (Dried Blood Spot), the test is non-invasive, rapid, specific and reliable. Briefly, a drop of blood is adsorbed on filter paper and left to dry at room temperature; the enzymatic activity is measured by a fluorimetric method. Genetic analysis is a solution to detect genetic variants in GAA gene. Moreover, genetic analysis is important to detect healthy carriers in the family context.

Since 2016 an enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is available for Pompe disease treatment. ERT is based on recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase administration. Our research team performs enzymatic and genetic assays necessary for PD diagnosis. The combination of biochemical and genetic analysis with clinical data allows to have a definitive and timely diagnosis for PD patients.
